Cervical health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being for women. The cervix, a small but vital part of the reproductive system, plays a significant role in a woman’s health and fertility.
Unfortunately, cervical cancer remains a prevalent threat, but the good news is that it is largely preventable. In this article, we will explore the importance of cervical health, risk factors for cervical cancer, and effective preventive measures that empower women to take control of their well-being.
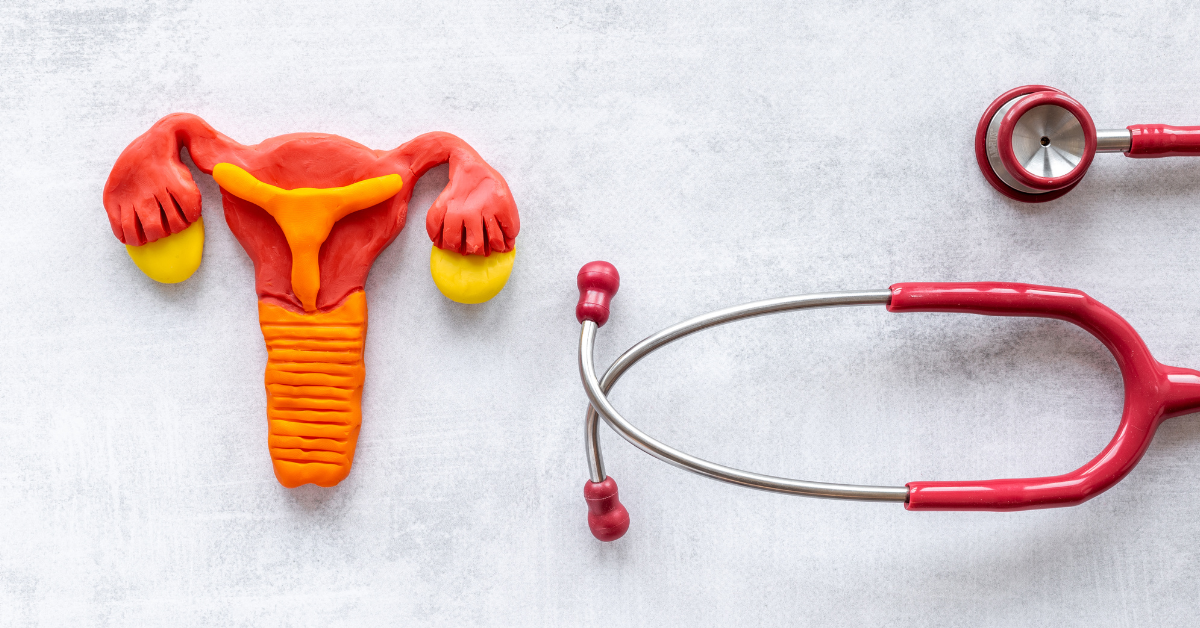

Understanding the Cervix:
The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It serves as a protective barrier and plays a key role during menstruation, pregnancy, and childbirth. Maintaining cervical health is essential for reproductive health and overall quality of life.
Cervical Cancer: A Preventable Threat:
Cervical cancer is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common virus transmitted through sexual contact. While most HPV infections clear on their own, persistent infections can lead to cervical cancer over time.
Key Risk Factors:
1. HPV Infection: The primary risk factor for cervical cancer is infection with high-risk HPV strains. Regular screenings can detect HPV and early changes in the cervix, allowing for timely intervention.
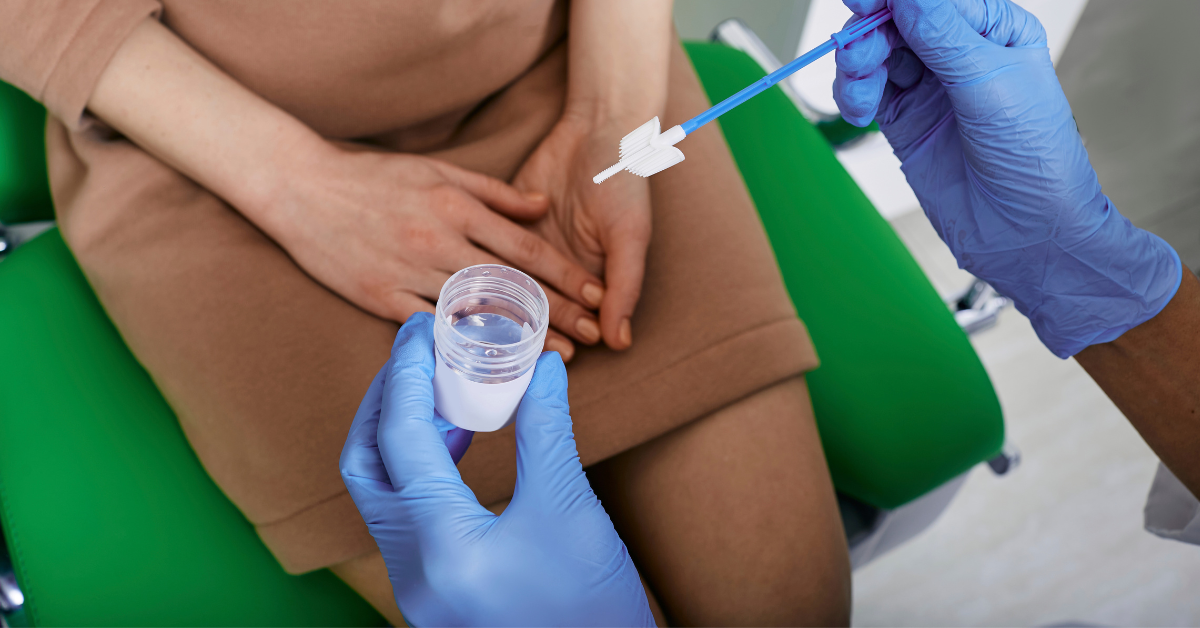
2. Lack of Regular Screenings: Women who do not undergo regular cervical screenings, such as Pap smears or HPV tests, are at an increased risk of developing cervical cancer. Screening detects abnormalities in the cervix before cancer develops.
3. Smoking: Tobacco use has been linked to an increased risk of cervical cancer. Quitting smoking not only benefits overall health but also reduces the risk of cervical cancer.
Preventive Measures:
1. Vaccination: The HPV vaccine is a powerful tool for preventing cervical cancer. Administered to pre-teens and teenagers, the vaccine protects against the most common high-risk HPV strains. It is essential to consult with healthcare providers to determine eligibility and the most appropriate vaccination schedule.
2. Regular Screenings: Pap smears and HPV tests are effective in detecting cervical abnormalities early on. Women are advised to undergo routine screenings as recommended by healthcare professionals. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, preventing the progression to cervical cancer.
3. Safe Sexual Practices: Practicing safe sex by using condoms and limiting sexual partners can reduce the risk of HPV transmission. Open communication with partners about sexual health is crucial.
4. Quit Smoking: For smokers, quitting is a critical step in preventing cervical cancer. Smoking cessation not only reduces the risk but also improves overall health.

Empowering Women through Education:
Empowering women with knowledge about cervical health and cancer prevention is crucial. Access to information, regular check-ups, and a proactive approach to health can significantly reduce the incidence of cervical cancer. By understanding the importance of screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle choices, women can take charge of their well-being and contribute to the prevention of cervical cancer.

